Sunburn is a form of skin damage caused by overexposure to ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun. A sunburn can develop after as little as 15 minutes in direct sunlight, depending on the time of year, time of day, and skin tone. Repeated overexposure and sunburning can lead to permanent skin damage and skin cancer.
All skin tones are susceptible to burning. The highest risk people for sunburn are those with blonde hair, blue eyes, fair and freckled skin. Darker skin tones have a lower risk of sunburn, but the risk is not zero. Black and Brown skin people are diagnosed with skin cancers, too.
A sunburn is characterized by red, painful skin that can be accompanied by swelling, itching, and blisters. The skin also feels warm for up to 24 hours following a sunburn.
Sunburns can range from mild to severe and can take up to several days to heal, depending on the depth of the burn. Sunburns damage the DNA of the skin, resulting in peeling and blisters. This damaged skin is no longer normal and sheds.
In extreme cases, sunburns can even cause permanent damage to the skin. Sunburns may result in skin discoloration such as:
–hypo or hyperpigmented patches
–melasma
–red, ruddy and thickened skin (poikeloderma) on the chest and neck
–solar lentigos / sun spots commonly seen on the face, chest, and hands
To prevent sunburn, it is important to wear sunscreen with an SPF of 30 or higher and to reapply accordingly. Mineral based SPFs are preferred. Mineral based SPF contain zinc and/or titanium which are minerals that provider a layer of physical protection on the skin. Chemical sunscreens offer good protection as well, but are less reliable in water and over longer periods of time spent in the sun. It is highly recommended that children, or adults with high risk for skin cancer, use a mineral based SPF.

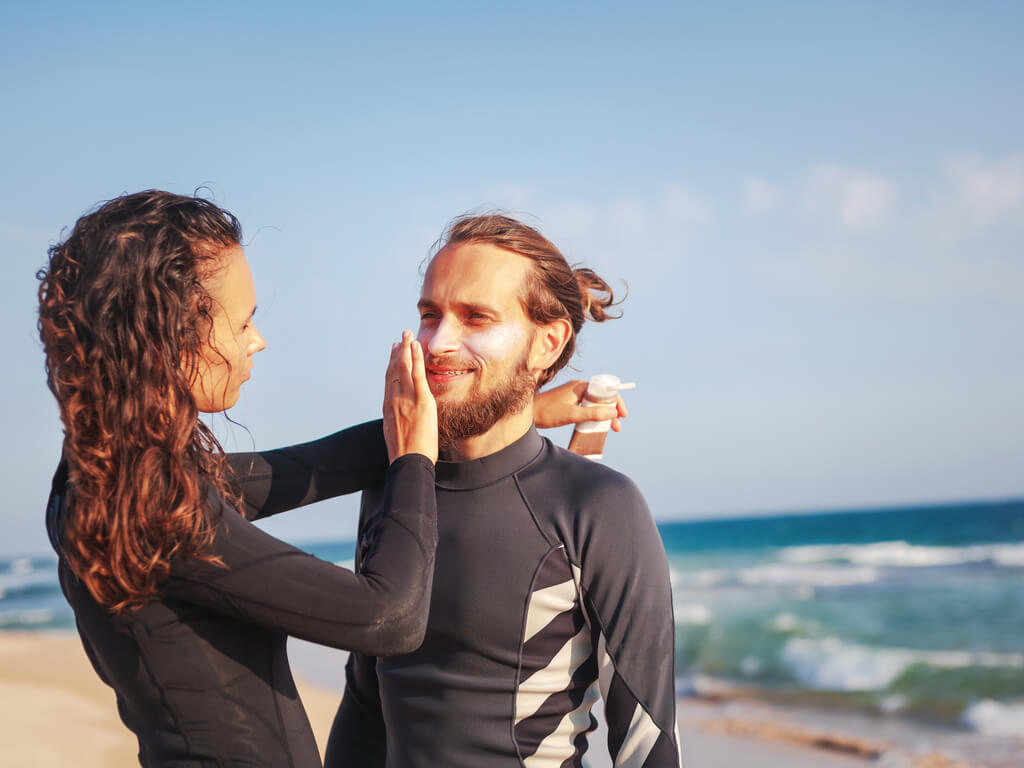
Wearing protective clothing such as a hat, sunglasses, rash guard or long-sleeved shirt can help protect your skin from UV damage. Protective clothing is preferable to SPF as it offers all day protection without reapplication. Additionally, avoid direct sunlight during peak hours of the day by seeking shade from a tree or an umbrella or tent.

It is important to stay hydrated and limit alcohol consumption when spending time in the sun. Taking these precautions can help you avoid the discomfort of sunburn and reduce your risk of developing skin cancer in the future.
Fortunately, there are a number of treatments available to help reduce the symptoms of sunburn and prevent further damage to your skin. These treatments include over-the-counter medications like acetaminophen and ibuprofen.
Extra hydration is also recommended. Moderate to severe sunburns require fluid to heal, therefore the fluid needs of the body are increased after a sunburn.
Home remedies such as cool baths and ice packs can cool the skin and relieve minor pain. Blistering sunburns may require medical intervention if the skin becomes infected. Seek medical care if symptoms worsen instead of improving.